Appendix G.Calculations From Three Strain Gauges, At 60 degrees, On a Circular Pipe
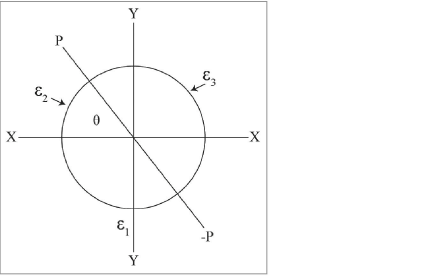
Figure 19: Three Strain Gauges Mounted on a Circular Pipe Diagram
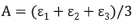
equation 17: Average Axial Strain
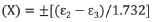
equation 18: Maximum Bending Strain Around the YY Axis

equation 19: Maximum Bending Strain Around the XX Axis
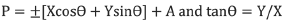
equation 20: Maximum Strain
Let 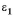 = 20,
= 20, 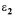 = 192 and
= 192 and 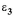 = 88 (all tensile strains)
= 88 (all tensile strains)
Average Axial Strain, A = (20 + 192 + 88) / 3 = 100 microstrain tension
X = ±(104 / 1.732) = ±60
Y = ±(300 / 3 - 20) = ±80
tanq = 80 / 60 = 1.333 and q = 53 degrees from the X axis
P = ±[60 x 0.6 + 80 x 0.8] + 100 = 200 microstrain, tensile, 0 microstrain minimum