1.Introduction
geokon Model 4420 vibrating wire crackmeters are designed to measure movement across tension cracks in soils, joints in rock and concrete, construction joints in buildings, bridges, pipelines, dams, and more.
The instrument consists of a vibrating wire sensing element in series with a heat-treated, stress-relieved spring, which is connected to the wire at one end and to a connecting rod at the other. The unit is fully sealed and operates at pressures of up to 250 psi. As the connecting rod is pulled out from the gauge body, the spring is elongated causing an increase in tension, which is sensed by the vibrating wire element. The increase in tension (strain) of the wire is directly proportional to the extension of the shaft. This change in strain allows the Model 4420 to measure the opening of the joint very accurately.
1:
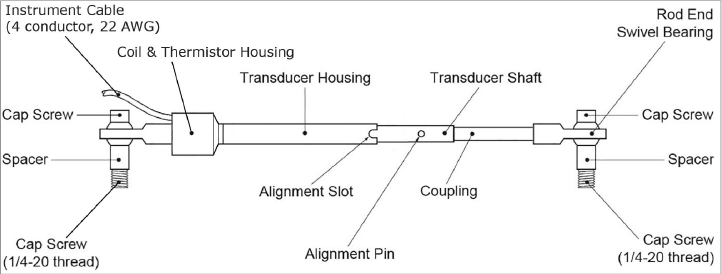
Figure 1: Model 4420 Vibrating Wire Crackmeter
Models 4420-3, 4420-12.5, and 4420-25 differ slightly from the standard crackmeter in that they provide for adjustment of the setting distance with a threaded extension rod and locking nut.
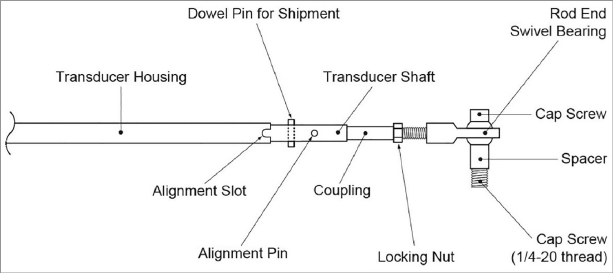
Figure 2: Model 4420-3, -12.5, -25 Detailed View
CAUTION! Do not rotate the shaft of the crackmeter more than 180 degrees: Doing so may cause irreparable damage to the instrument. Use the alignment pin on the transducer shaft and the slot on the body as a guide for alignment. Never extend the crackmeter beyond its working range.